CRO - Conversion Rate Optimisation
aka Even more regarding Online Marketing
CRO - Conversion Rate Optimisation, is the process of improving the efficiency of a website or application to encourage visitors to complete a desired action (conversion) more frequently. A conversion can mean different things depending on the type of website or business goals – for example, purchasing a product, filling out a form, subscribing to a newsletter, downloading an app, etc.
CRO increases return on investment (ROI) because, instead of focusing solely on attracting new visitors, CRO optimises conversions from existing visitors, which means better utilisation of current traffic.
CRO reduces customer acquisition costs: Improving the conversion rate could mean that you don't need to invest as much in acquiring new visitors.
It improves user experience: Enhancing the website to make it more user-friendly and easy to navigate helps not only conversions but also visitor satisfaction.
CRO focuses on increasing the percentage of visitors who take a specific action that the business desires (e.g., purchasing, signing up, submitting an inquiry). In simpler terms, it’s about making the site "friendlier" for users and simplifying the journey they need to take to do what you want.
For example, if you have an e-commerce site and the conversion rate is 2%, it means that out of every 100 visitors to your website, 2 people make a purchase. The goal of conversion rate optimisation is to increase this ratio.

- Improving User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX):
- Simplifying the navigation, layout, and design of the website so users can easily find what they’re looking for and aren't confused.
- Page load speed (faster pages have better conversion rates).
- A/B Testing:
- Testing two or more versions of a page or a part of a page (e.g., purchase buttons, forms, images) and comparing which version leads to a higher conversion rate.
- For example, testing different versions of the "Buy Now" button vs. "Add to Cart".
- Optimising Forms:
- Shortening forms to the minimum and removing unnecessary fields.
- Ensuring that forms are easy to fill out and that the visitor has a clear understanding of what will happen after submitting them (confirmation, next steps, etc.).
- Optimising Call-to-Action (CTA):
- Buttons and links that clearly prompt visitors to take action (e.g., "Buy Now", "Sign Up for Free", "Get a Discount").
- Buttons should be clearly visible and understandable, so users know the benefit of clicking them.
- Building Trust:
- Displaying reviews, ratings, security certificates, or guarantees on the site so users are confident that they are shopping safely and that the service is trustworthy.
- Example: "100% Safe Purchase" or "Guaranteed 30-Day Money-Back Guarantee".
- Simplifying the Purchase Process (for e-commerce sites):
- Allowing visitors to complete a purchase as quickly as possible, without unnecessary steps or complicated forms.
- For example, simplifying the cart and checkout process, adding options for fast checkout without registration, and offering multiple payment methods.
- Mobile Optimisation:
- Ensuring your website is fully functional and optimised for mobile devices. As more people shop or complete conversions on their phones, ensuring mobile-friendliness becomes even more important.
- Personalisation:
- Using data on user behaviour to personalise offers and communication. For example, recommending products based on previous purchases or viewed items.
What is SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
SEM (Search Engine Marketing), also known as marketing on search engines, is a form of digital marketing that focuses on increasing the visibility of websites in search engine results – primarily through paid advertising.
Main Tools and Platforms
- Google Ads – the most commonly used SEM tool (formerly Google AdWords)
- Bing Ads – ads in the Bing search engine (Microsoft Advertising)
- Seznam Sklik – the Czech alternative for advertising in the Seznam.cz search engine
Advantages of SEM
- Immediate results – ads appear almost instantly
- Precise targeting – based on keywords, location, device, etc.
- Measurability – clear statistics on performance
- Budget control – you pay only for actual clicks (PPC)
How SEM Works
- Create an ad in a platform like Google Ads.
- Choose keywords that will trigger your ad.
- Set a daily budget and cost per click (CPC).
- The ad is displayed to users searching for the relevant terms.
- You only pay when someone clicks on the ad.
SEM vs. SEO
| Feature | SEM (PPC Ads) | SEO (Organic Results) |
|---|---|---|
| Results | Quick | Long-term |
| Costs | Pay per click | Investment in content and time |
| Placement in Results | Above organic results | Below ads |
| Long-term Benefit | Temporary (ads disappear once stopped) | More permanent effect |
Examples of SEM Usage
- Online stores promoting specific products
- Local businesses (e.g., "plumber in London")
- Highly competitive services (e.g., lawyers, real estate agencies)
What is PPC (Pay-Per-Click)
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is an online advertising model where the advertiser pays for each click on their ad. It is an effective form of performance marketing because you only pay when a user shows interest in the offer by clicking on the ad.
How PPC Works
- Create an ad (e.g., in Google Ads).
- Choose keywords for which the ad will be displayed.
- Set the maximum cost per click (CPC).
- The ad will appear to users in search results or on partner websites.
- You only pay if someone clicks on the ad.
Most Common PPC Platforms
- Google Ads – the most widely used platform for PPC advertising in both search and display networks.
- Amazon Ads – for e-commerce stores and brands looking to promote products directly within Amazon.
- TikTok Ads – a rapidly growing platform targeting a younger audience.
- Facebook Ads – ads on the social network with the option to pay per click (CPC).
- LinkedIn Ads, Twitter Ads, Bing Ads – other alternatives for specific targeting.
- Seznam Sklik – a Czech tool for PPC advertising in the Seznam.cz search engine.
Advantages of PPC Advertising
- Quick launch – ads run almost immediately after approval.
- Budget control – you can start with small amounts and adjust the budget as needed.
- Precise targeting – based on location, device, interests, behaviour, etc.
- Measurability – detailed performance analytics available (CTR, CPC, conversions).
What to Watch Out For
- Traffic ≠ sales – monitor not only clicks but also conversions.
- Poorly set-up campaigns can quickly deplete the budget without results.
- PPC requires regular optimisation and testing for maximum effectiveness.
Everything You Need to Know About Google Ads
In the pay-per-click (PPC) advertising field, it is the most popular platform.
According to Statista data, it's search advertising revenue reached $40.69 billion, accounting for 28.6% of total digital revenue in the US.
The second is Facebook, but it is still significantly behind.
Why does it dominate the PPC market?
It’s simple: it is the most widely used search engine in the world, with a market share of approximately 83%. Bing lags behind with around 9% share.
Advertisers want to be where the users are – and Google has billions of them. That’s why it is one of the best places to focus your PPC strategy.
How Does it Work?
Google Ads works on a bidding system. Advertisers bid amounts for specific keywords to have their ads appear in search results.
The cost per click (CPC) can range from $1 to $500, depending on the industry. For example, law firms are willing to pay more because the return on a single conversion can be high.
Where Can You Advertise?
- Search Network: Displays text ads in search results. The advantage is high user intent – they are searching for a specific service or product.
- Display Network: Displays visual ads on partner websites, apps, and videos. It works well for brand building and remarketing.
- Remarketing: Allows you to re-engage users who have already visited your site but didn’t convert. Great for increasing chances of future conversions.
Why Use it?
- Fast results: Ads can appear immediately after launching the campaign.
- Precise targeting: Targeting by keywords, demographics, interests, and user behaviour.
- Measurement and optimisation: Access to analytics and campaign performance for continuous improvement.
- Budget control: Ability to set daily limits and maximum bids.
Other Useful Resources:
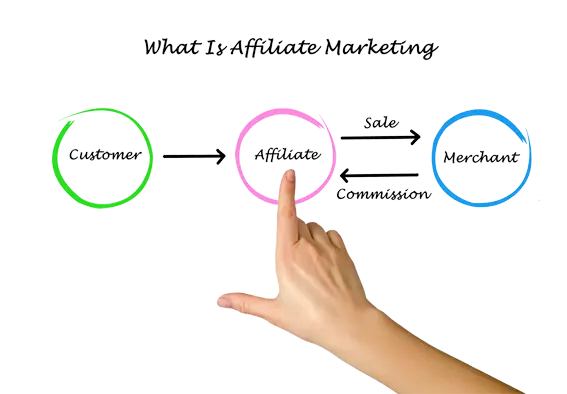
What is Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a form of performance marketing where companies collaborate with partners (called affiliates) who promote their products or services in exchange for a commission on a sale or other action taken.
How Affiliate Marketing Works
- The merchant launches an affiliate program.
- The affiliate registers and receives a unique tracking link.
- The affiliate promotes the products – for example, on a blog, website, social media, or newsletter.
- The user clicks on the link and makes a purchase (or takes another desired action).
- The affiliate receives a commission for the conversion made.
Benefits of Affiliate Marketing for Businesses
- You only pay for results (e.g. purchases, registrations).
- Low risk and costs – no conversion = no commission.
- The possibility of quickly expanding reach through a network of partners.
Benefits for Affiliate Partners
- The potential for passive income – for example, from a blog or social media.
- No need to have your own product or customer support.
- Work whenever and wherever – high flexibility.
Where Affiliate Marketing is Used
- Online stores – e.g. Alza, Notino, About You.
- Online services – such as Canva, Websupport, hosting companies.
- Digital products – e-books, online courses, software.
- Global affiliate networks – Amazon Associates, CJ Affiliate, ShareASale, ClickBank.
What is Content Marketing
Content marketing is a digital marketing strategy focused on creating and distributing valuable and relevant content aimed at attracting and retaining a target audience, and motivating them to take a desired action – such as making a purchase or registering.
Core Principles of Content Marketing
- Provide useful and valuable content that addresses customer needs.
- Build trust and authority without direct selling.
- Focus on long-term customer relationships, not just one-time conversions.
Content Marketing Formats
- Blog posts – educational or informational content that improves SEO.
- Videos – tutorials, reviews, interviews, stories.
- E-books and whitepapers – in-depth content often exchanged for contact details.
- Infographics – clear visualisation of data and information.
- Podcasts – audio content with expert or entertainment value.
- Case studies – examples of real-world successes and outcomes.
- Social media content – visual, short, or interactive formats.
Content Marketing Goals
- Increase organic website traffic.
- Build trust and relationships with customers.
- Improve search engine rankings (SEO).
- Generate leads.
- Support sales through indirect influence on decision-making.
Why Content Marketing Works
People are increasingly ignoring traditional advertising, but actively seeking information. Content marketing provides them with value – and brands that are useful are more likely to be trusted and successful.
What is Email Marketing

Email marketing is a form of direct digital communication with customers through email messages. It is used for building relationships, supporting sales, informing customers, and increasing loyalty.
Main Goals of Email Marketing
- Maintaining contact with customers.
- Supporting repeat purchases.
- Announcing news, promotions, or discounts.
- Automated customer care (e.g., welcome emails, abandoned cart reminders).
Advantages of Email Marketing
- Low cost – sending emails is cheaper than traditional advertising.
- Direct reach – it targets users who have consented to receive emails.
- High return on investment (ROI) – when done correctly, it is one of the most effective channels.
- Personalisation – messages can be customised based on customer behaviour and interests.
- Measurability – open rates, click-through rates, conversions, etc., can be tracked.
Types of Emails
- Newsletters – regular content with updates, tips, and news.
- Transactional emails – order confirmations, invoices, shipment tracking.
- Promotional emails – promotions, discounts, limited-time offers.
- Automated campaigns – e.g., welcome series, abandoned cart emails, birthday greetings.
Things to Watch Out For
- Always obtain opt-in consent (GDPR).
- Provide an easy unsubscribe option.
- Use a reliable and secure email marketing tool (e.g., Mailchimp, Ecomail, SmartEmailing).
